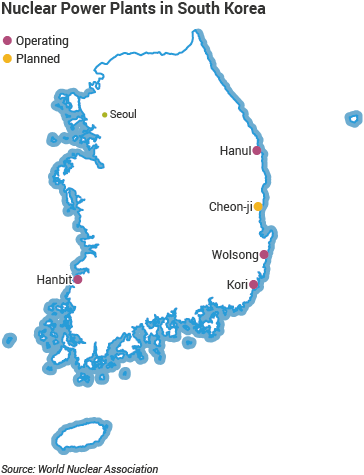
South Korea, which is roughly the size of Indiana, eventually became the most reactor-dense country in the world, with 23 reactors providing about 30% of the country’s total electricity generation…. South Korea’s reactors…are mostly packed into a narrow strip along the densely populated southeastern coast. The density was a way of cutting costs on administration and land acquisition. But putting reactors close to one another—and to large cities—was risky. …
In December 2009, the UAE had awarded a coalition led by Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) a $20 billion bid to build the first nuclear power plant in the UAE. Barakah was chosen as the site to build four APR-1400nuclear reactors successively. In 2012 to Park Geunhye the newly elected president pledged to increase South Korea’s reactor fleet to 39 units by 2035 and making sales trips to potential client states such as the Czech Republic and Saudi Arabia bulding on prior success like the UAE deal mentioned above. …
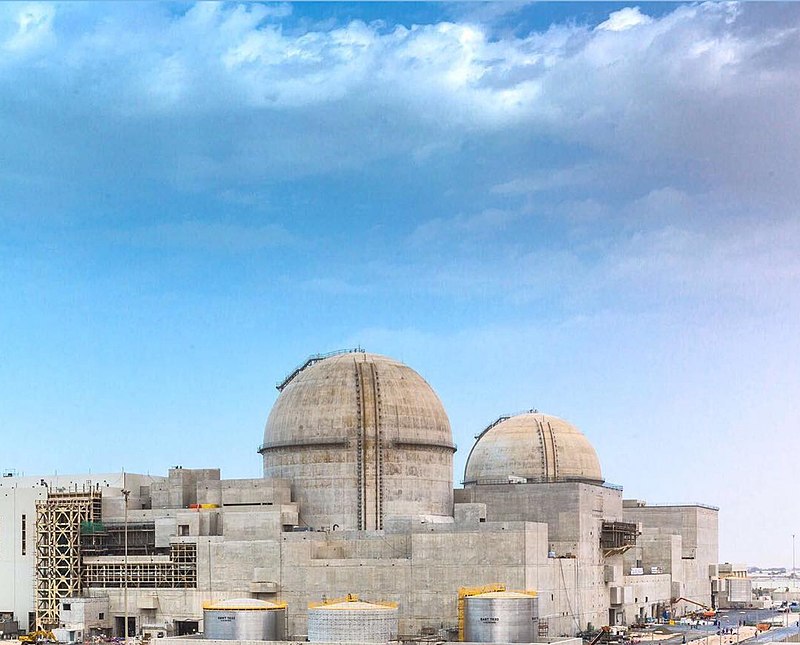

Barakah under construction in UAE
But on September 21, 2012, officials at Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP), a subsidiary of the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO), received an outside tip about illegal activity among the company’s parts suppliers. Eventually, an internal probe had become a full-blown criminal investigation. Prosecutors discovered that thousands of counterfeit parts had made their way into nuclear reactors across the South Korea, backed up with forged safety documents. KHNP insisted the reactors were still safe, but the question remained: was corner-cutting the real reason they were so cheap?
Park Jong-woon, a former manager who worked on reactors at KEPCO and KHNP until the early 2000s, believed so. He had seen that taking shortcuts was precisely how South Korea’s headline reactor, the APR1400, had been built…After the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, most reactor builders had tacked on a slew of new safety features.KHNP followed suit but later realized that the astronomical cost of these features would make the APR1400 much too expensive to attract foreign clients.“They eventually removed most of them,” says Park, who now teaches nuclear engineering at Dongguk University. “Only about 10% to 20% of the original safety additions were kept.” Most significant was the decision to abandon adding an extra wall in the reactor containment building—a feature designed to increase protection against radiation in the event of an accident. “They packaged the APR1400 as ‘new’ and safer, but the so-called optimization was essentially a regression to older standards,” says Park. “Because there were so few design changes compared to previous models, [KHNP] was able to build so many of them so quickly.”
Having shed most of the costly additional safety features, KEPCO was able to dramatically undercut its competition in the UAE bid, a strategy that hadn’t gone unnoticed. After losing Barakah to KEPCO, Areva CEO Anne Lauvergeon likened the Korean nuclear plant to a car without airbags and seat belts. At the time Lauvergeon’s comments were dismissed as sour words from a struggling rival.
By the time it was completed in 2014, the KHNP inquiry had escalated into a far-reaching investigation of graft, collusion, and warranty forgery; in total, 68 people were sentenced and the courts dispensed a cumulative 253 years of jail time. Guilty parties included KHNP president Kim Jong-shin, a Kepco lifer, and President Lee Myung-bak’s close aide Park Young-joon, whom Kim had bribed in exchange for “favorable treatment” from the government.
Several faulty parts had also found their way into the UAE plants, angering Emirati officials. “It’s still creating a problem to this day,” Neilson-Sewell, the Canadian advisor to Barakah, told me. “They lost complete faith in the Korean supply chain.”
Excerpts from Max S. Kim, How greed and corruption blew up South Korea’s nuclear industry, MIT Technology Review, April 22, 2019