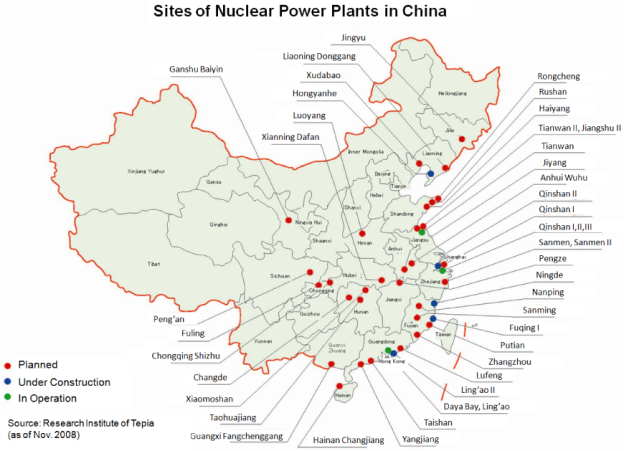
Nuclear power once seemed like the world’s best hope for a carbon-neutral future. After decades of cost-overruns, public protests and disasters elsewhere, China has emerged as the world’s last great believer, with plans to generate an eye-popping amount of nuclear energy, quickly and at relatively low cost.
The world’s biggest emitter, China’s planning at least 150 new nuclear reactors in the next 15 years, more than the rest of the world has built in the past 35. The effort could cost as much as $440 billion; as early as the middle of this decade, the country will surpass the U.S. as the world’s largest generator of nuclear power… It could also support China’s goal to export its technology to the developing world and beyond, buoyed by an energy crunch that’s highlighted the fragility of other kinds of power sources. Slower winds and low rainfall have led to lower-than-expected supply from Europe’s dams and wind farms, worsening the crisis, and expensive coal and natural gas have led to power curbs at factories in China and India. Yet nuclear power plants have remained stalwart…
And yet, even if China can develop the world’s most cost-effective, safe, flexible nuclear reactors, the U.S., India and Europe are unlikely to welcome their biggest global adversary into their power supplies. CGN has been on a U.S. government blacklist since 2019 for allegedly stealing military technology. In July, the U.K. began looking for ways to exclude CGN from its Sizewell reactor development. Iain Duncan Smith, Tory Member of Parliament, put it bluntly: “Nuclear is critical to our electric power, and we just can’t trust the Chinese.”
China’s ultimate plan is to replace nearly all of its 2,990 coal-fired generators with clean energy by 2060. To make that a reality, wind and solar will become dominant in the nation’s energy mix. Nuclear power, which is more expensive but also more reliable, will be a close third…Other countries would have to stretch to afford even a fraction of China’s investments. But about 70% of the cost of Chinese reactors are covered by loans from state-backed banks, at far lower rates than other nations can secure…
The most eager customer of China is Pakistan which, like China, shares a sometimes violently contested border with India. China’s built five nuclear reactors there since 1993, including one that came online this year and another expected to be completed in 2022. Other countries have been more hesitant. Romania last year canceled a deal for two reactors with CGN and opted to work with the U.S. instead.
Still, versions of China’s first homegrown reactor design, known as Hualong One, continue to operate safely in Karachi and Fujian province. And in September, China announced a successful test of a new, modular reactor that could be enticing overseas. China Huaneng Group Co. said it had achieved sustained nuclear reactions in a domestically designed, 200-megawatt reactor that heats helium, not water. By making the cooling process independent of external power sources, it should prevent the potential for the kind of massive meltdown that required the evacuation of more than 150,000 people in Fukushima. China’s modular reactors, if successful, wouldn’t require new power plant construction. In theory, they could replace coal-fired generators in existing thermal power plants…
Excerpts from Dan Murtaugh and Krystal Chia, China’s Climate Goals Hinge on a $440 Billion Nuclear Buildout, Bloomberg, Nov. 2, 2021