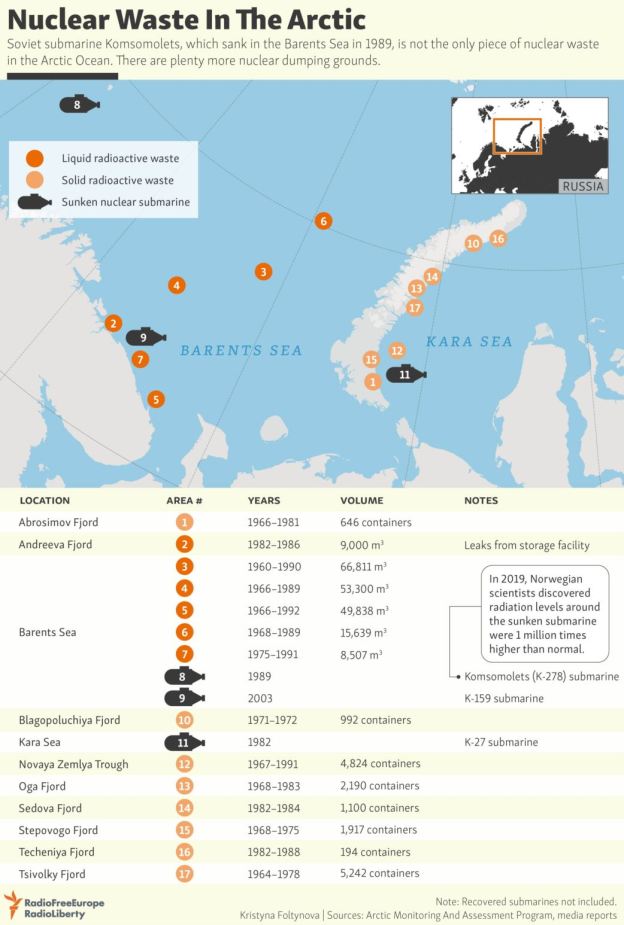
“When using fast reactors in a closed fuel cycle, one kilogram of nuclear waste can be recycled multiple times until all the uranium is used and the actinides — which remain radioactive for thousands of years — are burned up. What then remains is about 30 grams of waste that will be radioactive for 200 to 300 years,” said Mikhail Chudakov, IAEA Deputy Director General and Head of the Department of Nuclear Energy.
Fast reactors were among the first technologies deployed during the early days of nuclear power, when uranium resources were perceived to be scarce. However, as technical and material challenges hampered development and new uranium deposits were identified, light water reactors became the industry standard. However, efforts are underway in several countries to advance fast reactor technology, including in the form of small modular reactors (SMRs) and microreactors (MRs).
Five fast reactors are now in operation: two operating reactors (BN-600 and BN-800) and one test reactor (BOR-60) in the Russian Federation, the Fast Breeder Test Reactor in India and the China Experimental Fast Reactor. The European Union, Japan, the United States of America, the United Kingdom and others have fast reactor projects tailored to a variety of aims and functions underway, including SMRs and MRs. Russia’s Pilot Demonstration Energy Complex, which is under construction in Seversk, brings together a lead-cooled BREST-OD-300 fast reactor, a fuel fabrication and refabrication plant, and a plant for reprocessing mixed nitride uranium–plutonium spent fuel. A deep geological waste repository will also be built. The importance of this pilot project is not only to demonstrate the making of new fuel, irradiate it, and then recycle it, but to do so all on one site.
“Having the whole closed fuel cycle process on one site is good for nuclear safety, security and safeguards,” said Amparo Gonzalez Espartero, Technical Lead for the Nuclear Fuel Cycle at the IAEA. “It should also make more sense economically as the nuclear waste and materials do not need to be moved between locations — as they are currently in some countries — thereby minimizing transportation and logistical challenges.”
Projects are advancing in other countries. China is constructing two sodium cooled fast reactors (CFR-600) in Xiapu County, Fujian province. The first unit is under commissioning and is expected to be connected to the grid in 2024. In the USA, a fast reactor project backed by Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates is under development; it will not operate in a closed fuel cycle, although the country is renewing efforts to work on closed nuclear fuel cycles and use its existing nuclear waste to develop its own supply of fuel. In Europe, the MYRRHA project in Belgium is aimed towards building a lead-bismuth cooled accelerator driven system by 2036 to test its ability to break down minor actinides as part of a future fully closed fuel cycle.
Excerpts from Lucy Ashton, When Nuclear Waste is an Asset, not a Burden, IAEA, Sept., 2023