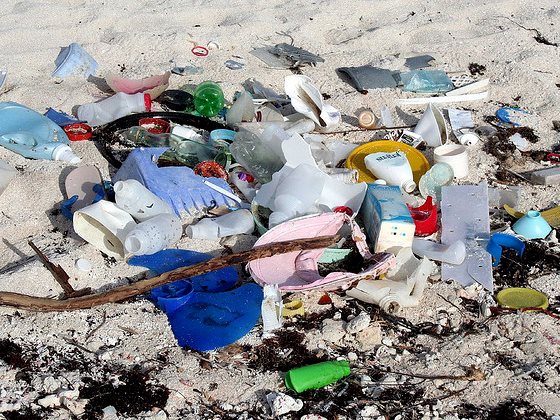
Plastic pollution has become one of the major global environmental challenges of the century; projections show that by 2050 the oceans may have more plastic than fish. Nuclear technology has emerged as one innovative solution to this growing problem. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has been working on an initiative called Nuclear Technology for Controlling Plastic Pollution – NUTEC Plastics.
Nuclear technology can be used to innovate plastic waste recycling and support development of biodegradable, green alternatives to single use petroleum-based plastic products – an approach aimed at reducing the volume of plastic waste world-wide and prevent the plastics from reaching earth’s marine environments. Nuclear techniques can also be used to quantify and characterize marine microplastic pollution and to assess their impact on coastal and marine ecosystems. A global plastics monitoring network of marine laboratories can also help tackle marine pollution. Presently, there are 55 laboratories in the global NUTEC Plastics Monitoring Network. ..
The Philippines has a significant plastic pollution problem and a great interest in recycling. The Department of Science and Technology (DOST) in the Philippines has undertaken a pre-feasibility study for a pilot plant employing electron beam radiation to combine two waste streams – plastics and palm tree fibers – into a new consumer product, construction material…
The IAEA is unique within the United Nations system in having laboratories in Austria and Monaco that apply nuclear science to help states address some of the world’s biggest issues, including plastic pollution… The Monaco laboratories serve as the central hub to the global NUTEC Plastics Monitoring Network.
Excerpts from Sinead Harvey, More Plastic Than Fish by 2050 – IAEA Event Gathers Experts Working Together to Save Marine Environments from Plastic Pollution, IAEA Newsletter, Sept. 28, 2022