Northern Norway saw a record number of 12 visiting NATO nuclear-powered submarines in 2018. The subs are in for supplies or crew change before continuing the cat-and-mouse hunt for Russian submarines sailing out in the strategically important waters between Norway, Iceland and Greenland. It was here, in international waters outside Senja in Troms, the Russian Echo-II class submarine K-192 suffered a severe reactor coolant accident 30 years ago, on June 26th 1989. Radioactive iodine was leaking with the reactor-steam while the vessel was towed around the coast of northernmost Norway to the navy homeport at the Kola Peninsula.
Fearing similar accidents could happen again, Norway is pushing for international awareness to..A dedicated group, named ARCSAFE, was established under the Arctic Council in 2015 aimed at sharing knowledge and experiences between national radiation authorities and other rescue services.“Norway has suggested to form an expert group, where one of the tasks could be to look into a possible Arctic Council agreement for radiation emergencies, like already exists for oil spill and search- and rescue cooperation,” says Øyvind Aas-Hansen.
Meanwhile, international experts on radiation monitoring teamed up with industry developers looking at the potential for using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in the Arctic. …Some environments are too risky for humans to survey and collect data. A nuclear accident site is one such spot, also if it happens at sea. UAVs, better known as drones, could carry a geiger counter, camera or other tools in the air over hazardous objects like a submarine on fire. From safe distance, emergency response units could then be better prepared before boarding or sailing close-up.
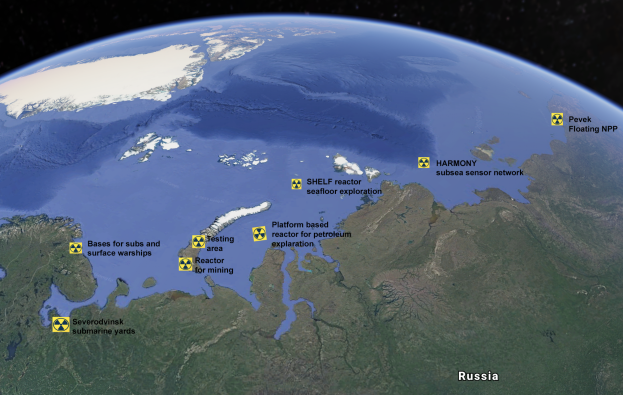
The Barents Observer has recently published an overview listing the increasing number of reactors in the Russian Arctic. According to the list there are 39 nuclear-powered vessels or installations in the Russian Arctic today with a total of 62 reactors. This includes 31 submarines, one surface warship, five icebreakers, two onshore and one floating nuclear power plants. Looking 15 years ahead, the number of ships, including submarines, and installations powered by reactors is estimated to increase to 74 with a total of 94 reactors, maybe as many as 114. Additional to new icebreakers and submarines already under construction, Russia is brushing dust of older Soviet ideas of utilizing nuclear-power for different kind of Arctic shelf industrial developments, like oil- and gas exploration, mining and research. “By 2035, the Russian Arctic will be the most nuclearized waters on the planet,” the paper reads.
Other plans to use nuclear reactors in the Russian Arctic in the years to come include many first-of-a-kind technologies like sea-floor power reactors for gas exploration, civilian submarines for seismic surveys and cargo transportation, small-power reactors on ice-strengthen platforms.
In the military sphere, the Arctic could be used as testing sites for both Russia’s new nuclear-powered cruise-missile and nuclear-powered underwater weapons drone. Both weapons were displayed by President Vladimir Putin when he bragged about new nuclear weapons systems in his annual speech to the Federation Council last year.
For Norway and Russia, a nuclear accident in the Barents Sea could be disastrous for sales of seafood. The two countries export of cod and other spices is worth billions of Euros annually.
Excerpts from Arctic countries step up nuclear accident preparedness, Barents Observer, June 30, 2019.