The shining light that was once Japan’s renewable energy industry is beginning to dim as reality sets in and it faces competition from a rejuvenated nuclear power industry…According to a February nationwide survey by the Japan Renewable Energy Foundation, 34 of the 79 solar energy producers who responded said they had given up on at least one solar power project. Roughly 45 percent of those respondents cited difficulties in land procurement, followed by 25 percent who said they had problems joining the power grid.
One such project in Hokkaido, located near the New Chitose Airport, called for a 100-hectare solar power generation facility. The site adjacent to the Abiragawa river remains covered in weeds to this day. “We call it an April 17 crisis,” said Hiroaki Fujii, the 43-year-old executive vice president at SB Energy Corp., a Tokyo-based company that designed the plans. On that date this year, Hokkaido Electric Power Co. said it would only purchase a total of 400 megawatts of electricity as part of the feed-in tariff system from the so-called mega-solar power plants, each with a generation capacity of 2 megawatts or more. That amounts to turning down as many as 70 percent of the 87 applications to sell it power, filed through March, with a combined output capacity of 1.568 gigawatts. One Hokkaido Electric official justified the decision: “Our power grid has a limited capacity. Accepting too much power from solar plants, where output levels fluctuate wildly depending on the weather, compromises a stable supply of electricity.”
One Sapporo-based real estate company lost money speculating. The company purchased two plots of land to host solar power plants that never materialized. “We were taken in by a renewable energy bubble,” the company’s president lamented.
The renewable energy feed-in tariff system was introduced in July 2012. It obligates utilities to purchase electricity generated by solar and wind plants at predetermined prices. The then-ruling Democratic Party of Japan initiated the system in a bid to bolster the nation’s renewable energy production, which accounted for less than 2 percent of the total power generation at the time, to 30 percent.
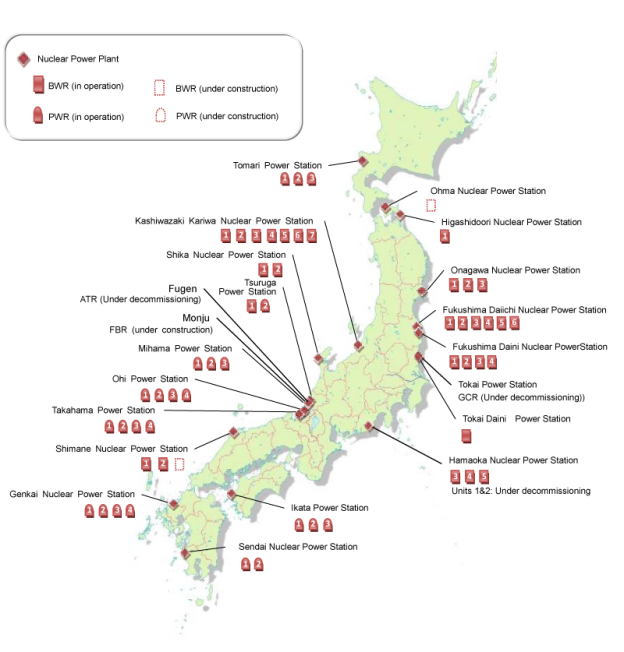
The regional utility’s decision to limit its purchases of solar power cannot be assigned to grid capacity alone. The decision was taken in large part due to Hokkaido Electric’s expectations that all three idled reactors at its Tomari nuclear power plant will eventually go back online…But if utilities revert to relying on nuclear power to levels before the Fukushima disaster, that could leave very little room for the emerging renewable energy industries to grow.
Enter the savior of Japan’s nuclear energy sector: Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s growth strategy. The Abe administration is eager to export Japan’s nuclear technologies and expertise. Not only did his government help secure a contract to build nuclear reactors in Turkey, but Abe himself, acting as the country’s top salesman, visited Saudi Arabia, India and Central Europe to promote Japanese nuclear capabilities. In late March, a group representing the Japan Atomic Industrial Forum (JAIF) also visited the Sizewell nuclear power plant 160 kilometers northeast of London. The forum’s constituent members include power utilities and manufacturers dealing in nuclear technologies. There are plans to build two more nuclear reactors on the grounds of the Sizewell site.
“Expanding our nuclear operations overseas has come to play a larger role in our perspective since the Abe administration came to power,” said Akihiro Matsuzaki, an official in the JAIF Department of International Affairs and a member of the mission to Sizewell. Foundation work is already under way there. Hitachi Ltd., which acquired Britain’s Horizon Nuclear Power Ltd., said it also hopes to boost the annual sales of its nuclear business division from the current 160 billion yen ($1.64 billion) to 360 billion yen by fiscal 2020. “We will be part of Abenomics (Abe’s economic policy),” Hitachi Senior Vice President Tatsuro Ishizuka told a briefing session for investors on June 13.
MARI FUJISAKI, Japan’s growth in renewable energy dims as nuclear strives for comeback, Asahi Shimbun July 7, 2013